Board( List<Board> )
Board ( Dto )
package sec02.exam01;
public class Board {
private String title;
private String content;
public Board(String title, String content) {
super();
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
}
Board ( Dao )
package sec02.exam01;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class BoardDao {
public List<Board> getBoardList(){
List<Board> list = new ArrayList<Board>();
list.add(new Board("제목1", "내용1"));
list.add(new Board("제목2", "내용2"));
list.add(new Board("제목3", "내용3"));
return list;
}
}
실행
package sec02.exam01;
import java.util.List;
public class ListEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BoardDao dao = new BoardDao();
List<Board> list = dao.getBoardList();
for(Board board : list) {
System.out.println(board.getTitle() + "_" + board.getContent());
}
}
}
<결과>
제목1_내용1
제목2_내용2
제목3_내용3
Set / HashSet
hashCode()와 equals() 재정의
package sec02.exam02;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Student {
public int studentNum;
public String name;
public Student(int studentNum, String name) {
super();
this.studentNum = studentNum;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(studentNum);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
return studentNum == other.studentNum;
}
}
실행 ( Student 중복 저장 방지 )
package sec02.exam02;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashSetEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Student> set = new HashSet<Student>();
set.add(new Student(1, "홍길동"));
set.add(new Student(2, "신용권"));
set.add(new Student(1, "조민우")); // 학번이 같아서 저장되지 않음
Iterator<Student> iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Student student = iterator.next();
System.out.println(student.studentNum + ":" + student.name);
}
}
}
<결과>
1:홍길동
2:신용권
Map<>, HashMap<> / 점수 관리 ( 평균, 최고점수, 최고점수를 받은 학생 아이디 )
package sec02.exam02;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("blue", 96);
map.put("hong", 86);
map.put("white", 92);
String name = null;
int maxScore = 0;
int totalScore = 0;
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrySet) {
if(entry.getValue()>maxScore) {
name = entry.getKey();
maxScore = entry.getValue();
}
totalScore += entry.getValue();
}
int avgScore = totalScore / map.size();
System.out.println("평균점수: " + avgScore);
System.out.println("최고점수: " + maxScore);
System.out.println("최고점수를 받은 아이디: " + name);
}
}
<결과>
평균점수: 91
최고점수: 96
최고점수를 받은 아이디: blue
LIFO와 FIFO 컬렉션
LIFO : Last IN First Out ( 후입선출 ) 은 나중에 넣은 객체가 먼저 빠져나가는 자료구조
FIFO : First IN First Out ( 선입선출 ) 은 먼저 넣은 객체가 먼저 빠져나가는 자료구조
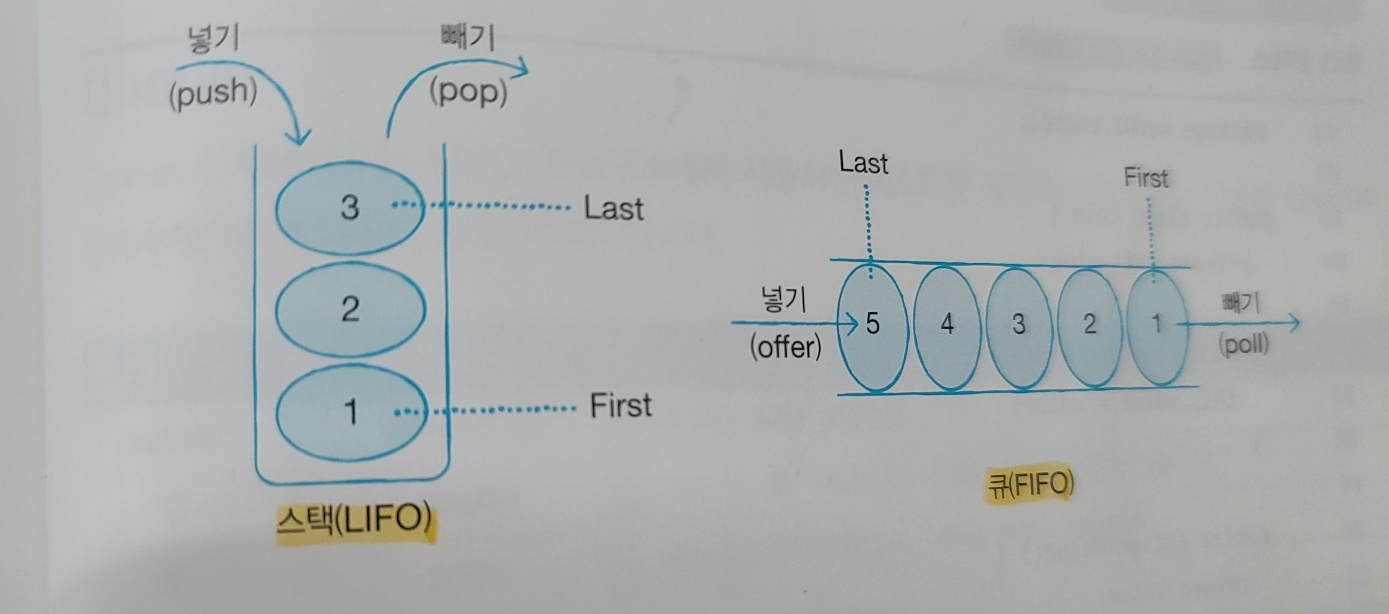
Stack
Stack은 LIFO 자료구조를 구현한 클래스
리턴 타입은 모든 메소드가 E ( Stack<E )
Push(E item) 메소드는 객체를 스택에 넣는다.
peek() 스택 맨 위 객체를 가져옴 / 객체를 스택에서 제거하지 않음
pop() 스택 맨 위 객체를 가져옴 / 객체를 스택에서 제거
Coin 예제
정의
package sec02.exam03;
// 스택 예제
public class Coin {
private int value;
public Coin(int value) {
super();
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
}
실행
package sec02.exam03;
import java.util.Stack;
//스택 예제
public class CoinEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Coin> coinBox = new Stack<Coin>();
coinBox.push(new Coin(100));
coinBox.push(new Coin(50));
coinBox.push(new Coin(500));
coinBox.push(new Coin(10));
Coin coin1 = coinBox.pop();
System.out.println("꺼내온 동전 = " + coin1.getValue()+ "원" );
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------");
while(!coinBox.isEmpty()) {
Coin coin = coinBox.pop();
System.out.println("꺼내온 동전 = " + coin.getValue()+ "원" );
}
}
}
<결과>
꺼내온 동전 = 10원
-----------------------------------------------
꺼내온 동전 = 500원
꺼내온 동전 = 50원
꺼내온 동전 = 100원
Queue( 큐 )
Queue 인터페이스는 FIFO 자료구조에서 사용되는 메소드를 정의하고 있다.
리턴 타입 boolean 메소드는 offer(E e) 주어진 객체를 넣는다.
리턴 타입 E peek() 객체 하나를 가져온다. 객체를 큐에서 제거하지 않는다.
리턴 타입 E poll() 객체 하나를 가져온다. 객체를 큐에서 제거한다.
Queue 인터페이스를 구혀한 대표적인 클래스는 LinkedList
Queue 큐 메시지 보내기 예제
선언
package sec02.exam04;
public class Message {
// Queue 큐
public String command;
public String to;
public Message(String command, String to) {
super();
this.command = command;
this.to = to;
}
}
실행
package sec02.exam04;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Queue 큐
Queue<Message> messageQueue = new LinkedList<Message>();
messageQueue.offer(new Message("sendMail", "홍길동"));
messageQueue.offer(new Message("sendSMS", "신용권"));
messageQueue.offer(new Message("sendKakaotalk", "홍두께"));
while(!messageQueue.isEmpty()) { // 메시지 큐가 비었는지 확인
Message message = messageQueue.poll();// 메시지 큐에서 1개의 메시지 꺼냄
switch (message.command) {
case "sendMail":
System.out.println(message.to + "님에게 메일을 보냅니다.");
break;
case "sendSMS":
System.out.println(message.to + "님에게 SMS를 보냅니다.");
break;
case "sendKakaotalk":
System.out.println(message.to + "님에게 카카오톡을 보냅니다.");
break;
}
}
}
}
<결과>
홍길동님에게 메일을 보냅니다.
신용권님에게 SMS를 보냅니다.
홍두께님에게 카카오톡을 보냅니다.